Snore Lase
The Mechanism of Snoring
The Mechanism of Snoring

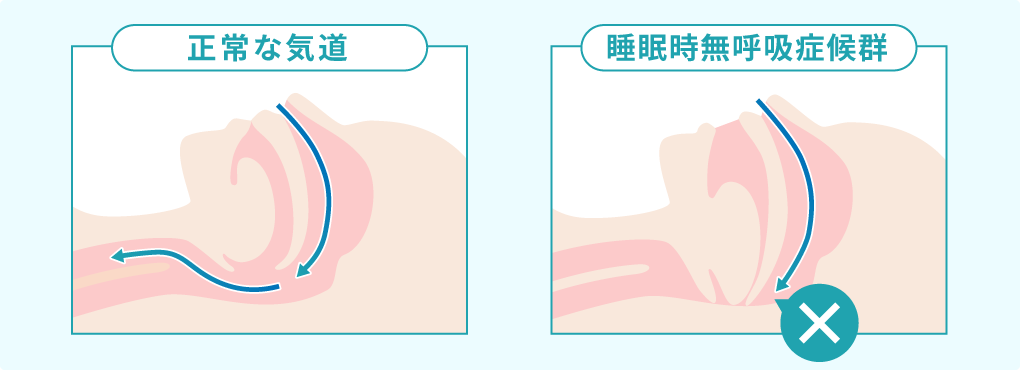
Snoring is the sound produced when soft tissues in the upper airway vibrate during sleep. T
he main cause is narrowing or obstruction of the airway. During sleep, muscles relax and the tongue root, soft palate, and pharyngeal walls fall backward, narrowing the airway. When air passes through this narrowed space, surrounding soft tissues vibrate, producing snoring sounds.

The volume and frequency of snoring changes depending on the degree of airway narrowing. In mild cases, it’s just snoring, but when severe, it can lead to sleep apnea syndrome.
Factors contributing to snoring include obesity, aging, alcohol consumption, sleeping medication use, nasal congestion, enlarged tonsils, enlarged tongue, and jaw abnormalities.
Particularly, sleeping on one’s back tends to worsen snoring due to gravity causing the tongue root to fall backward.
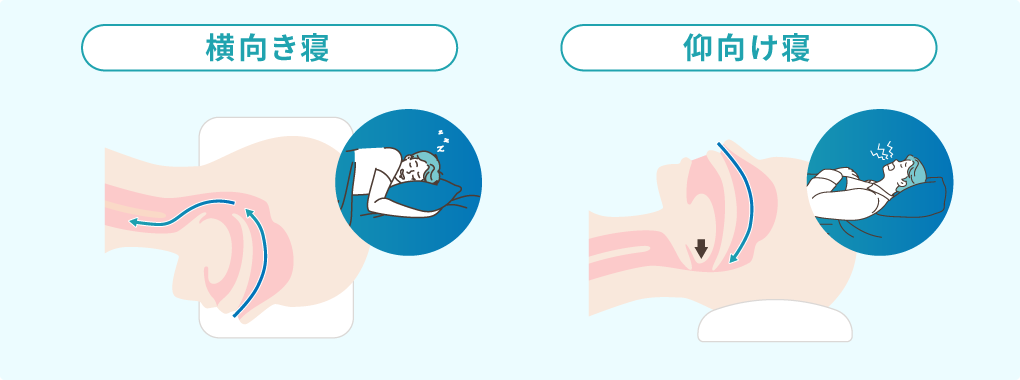
To improve snoring, it is important to address these factors. Lifestyle improvements, weight management, and maintaining proper sleeping positions are effective measures.
Snoring is a Sign of Sleep Apnea Syndrome
Snoring often serves as an important warning sign of Sleep Apnea Syndrome (SAS).
While not all snoring indicates SAS, loud and irregular snoring requires attention. In SAS, breathing repeatedly stops or decreases during sleep.
This occurs due to upper airway obstruction, and snoring is also related to this obstruction.
Most SAS patients snore loudly, but the characteristic feature is sudden loud gasping or snoring sounds after breathing stops.
The characteristics of snoring may suggest SAS.
 Loud and irregular snoring
Loud and irregular snoring Breathing interruptions or sounds of struggling to breathe
Breathing interruptions or sounds of struggling to breathe Snoring accompanied by excessive daytime sleepiness
Snoring accompanied by excessive daytime sleepiness Snoring accompanied by frequent nighttime awakenings
Snoring accompanied by frequent nighttime awakenings
When these symptoms are present, it is important to consider the possibility of SAS and receive a diagnosis from a specialist. Early detection and appropriate treatment reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease and high blood pressure, and improve quality of life.
Sleep Apnea Syndrome is Commonly Seen in Middle-aged and Older Men
In Japan, approximately 60% of people who snore are middle-aged and older men, and it is estimated that 30-40% of them have sleep apnea syndrome.
Additionally, sleep apnea syndrome affects about 9% of men and about 3% of women, and research results show that such individuals have about 2.4 times more accident experiences due to sleep deprivation.
Many people go without treatment, but we recommend seeking treatment early before serious accidents such as traffic accidents occur.
please feel free to consult with us first.
Physical Risks from Sleep Apnea Syndrome
SAS is not just a sleep disorder, but a condition that can have serious effects on the entire body. The main risks are as follows:

- High blood pressure
- Arrhythmia
- Myocardial infarction
- Stroke

- Diabetes
- Metabolic
syndrome

- Depression
- Cognitive decline
- Memory impairment

- Increased risk of traffic accidents
- Decreased work efficiency
- Risk of occupational accidents

- Chronic fatigue
- Sexual dysfunction
- Interference with social life

- Liver dysfunction
- Weakened immune system
These risks increase according to the severity and duration of SAS. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many risks can be reduced or prevented. Early detection and early treatment are extremely important.
Our Non-Surgical Snoring Laser Treatment ‘Snore Lase’

The non-surgical snoring laser treatment ‘Snore Lase’ was invented as a non-invasive and effective method. The main advantages of treating snoring with Snore Lase treatment include the following:
- Minimal pain (with topical anesthesia)
- Outpatient treatment is possible with almost no downtime
- Low risk of side effects
Snore Lase treatment applies laser to the soft palate and uvula, which are the sources of snoring, heating the tissue without removing the uvula or soft palate as in insurance-covered uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) or laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP).
The machine used is specifically designed for laser irradiation with protocols dedicated to snoring treatment.
Our Snore Lase treatment provides customized treatment by adjusting the irradiation settings according to each patient’s individual condition.
Snore Lase Laser Treatment Process and Mechanism of Action
-
–01–
Cleaning the Oral Cavity
 Cleaning the Oral Cavity
Cleaning the Oral Cavity
-
–02–
Spraying Anesthetic on the Irradiation Area
 Spraying Anesthetic on the Irradiation Area
Spraying Anesthetic on the Irradiation Area
-
–03–
Laser Irradiation
(Approximately 15 minutes)
 Laser Irradiation
Laser Irradiation
(Approximately 15 minutes)Collagen Contraction Soft tissue tightens and the airway widens
New Collagen Production Tissue elasticity improves
Hardening of Submucosal Tissue Suppresses vibration -
–04–
Return Home
 Return Home
Return Home
Through these actions, airway patency is improved and vibration of soft tissues that cause snoring is reduced. Treatment is performed in multiple sessions, with effects appearing gradually.
Laser treatment is less invasive and safer compared to surgery, making it an attractive option for many patients.
However, whether Snore Lase treatment is applicable is determined by a specialist doctor after examining individual symptoms and causes, so please feel free to consult with our clinic first.


